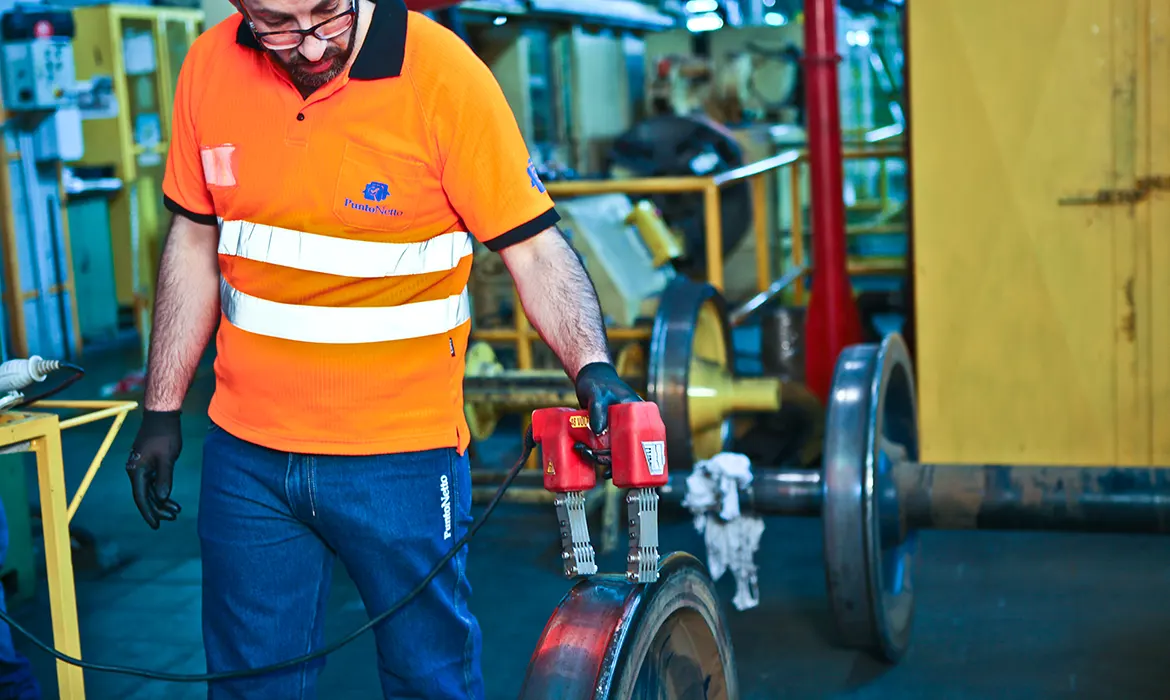
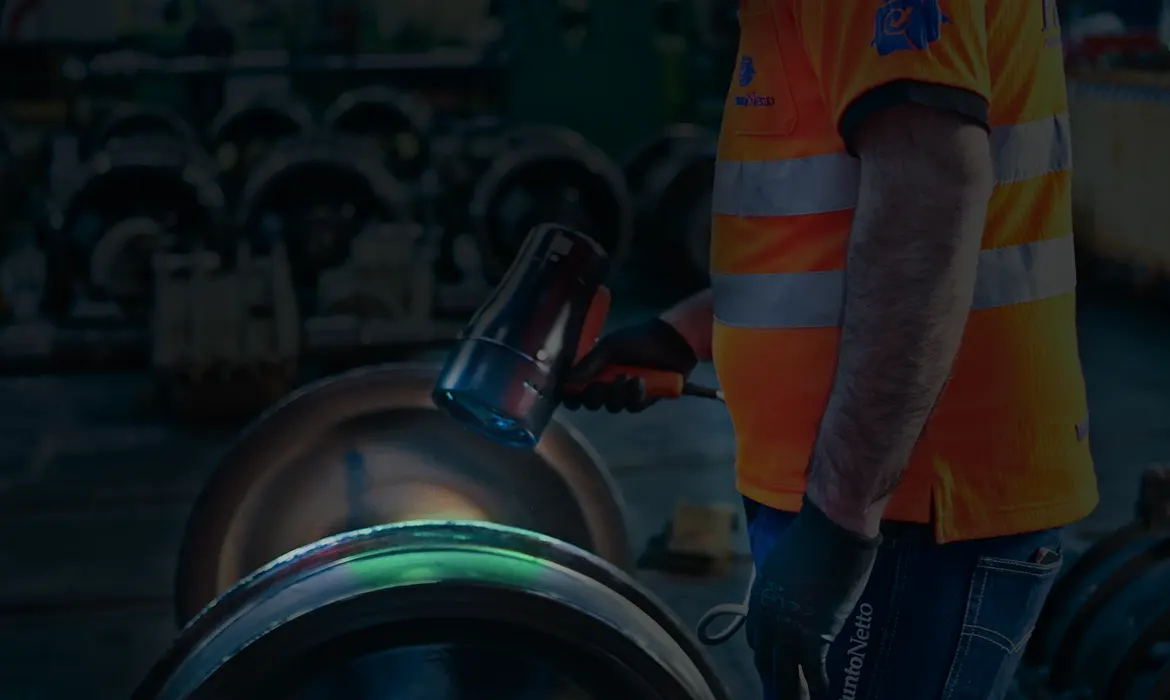
News: One of the most qualified and specific non-destructive tests in order to carry out an accurate verification of tig weldings is Magnetoscopy. The control is based on the analysis of variations in magnetic particles, which occur in the presence of surface or sub-surface defects.
FOCUS ON MAGNETOSCOPY
The Magnetoscopic test - which in Italy is erroneously also known as Magnaflux control, from the name of one of the best known magnetoscopes bench - exploits the magnetic properties of ferrous materials to detect any discontinuity in Tig weldings.The presence of cracks or other defects generated by industrial weldings causes a distortion of the lines of force of the tangential magnetic field. In this way the magnetic particles are grouped at the discontinuity, highlighting the defect. The particles, in the case of fluorescent use, are displayed with the use of a UV light lamp.
Among our non-destructive tests on Tig weldings, those performed with the Magnetoscope can only find application on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, nickel, cobalt and some of their alloys. The physical principle on which the control is based is magnetism, which represents a force field generated by the presence of direct or alternating electric currents.
THE 5 PHASES OF MAGENTOSCOPY

The non-destructive tests carried out in the Magnetoscopyregime on Tig weldings, follow a very precise scheme declined in 5 steps:
1) Surface preparation;
2) Magnetization of the piece;
3) Application of magnetic powder;
4) Lighting and surface inspection;
5) Demagnetization of the piece (optional).
HOW MAGNETOSCOPY WORKS
For the magnetic particle test the magnetic yoke is a fundamental tool. It is portable, easy to use on site and consists of an electric coil winding around a U-shaped in soft iron body that acts as an electro-magnet.
The current passage generates the magnetic field. The U shape allows for quick and easy positioning on the welded part to be checked. The poles of the electromagnet can be fully articulated, this allows the use of the magnetic yoke for the control of pieces having different shapes and sizes without compromising the sensitivity of the test.
The Magnetoscope can use both alternating and direct current. Direct current ensures greater penetration while alternating current concentrates the magnetic field on the surface of the workpiece, providing good sensitivity for detecting surface discontinuities in a relatively small area.
If you want to learn even more about the aspects of Magnetoscopy, then go to our MORE INFORMATION ON MAGNETOSCOPY



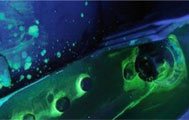 Among the many services provided by Equity Point stand out the non-destructive testing, with Penetrating liquids, Ultrasound and Magnetic Particle.
Among the many services provided by Equity Point stand out the non-destructive testing, with Penetrating liquids, Ultrasound and Magnetic Particle.